A 62 Year Old Man With Alcohol Induced Liver Disease
A 62 year old man with alcohol induced liver disease. Serum urate 074 mmolL 023-046 What would be the most useful additional biochemistry test to perform in this situation. The liver contributes to the metabolism of ingested food and provides the fluids that the GI tract requires. LDH Question 3 A 30-year-old obese male was found elevated ALT and ALP.
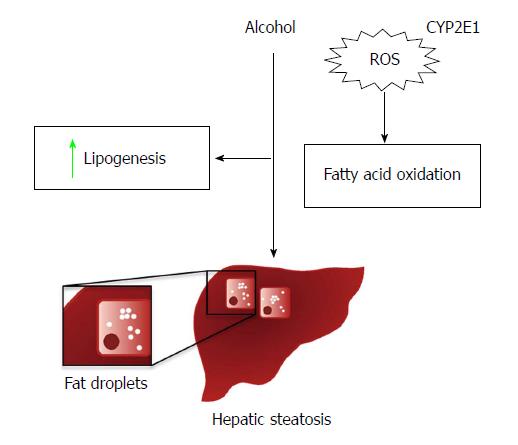
This can cause your liver to become enlarged. Over time scarring and cirrhosis can occur. It is usually asymptomatic and is completely reversible once you stop drinking alcohol.
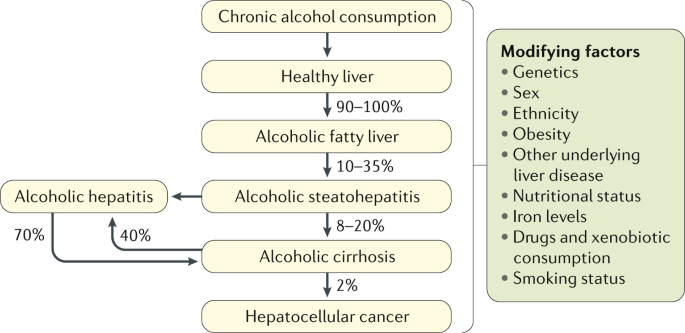
There are 3 types. Fatty liver is a universal finding among heavy drinkers and up to 40 of those with moderate alcohol intake 10-80 mgday also exhibit fatty liver changes. A 62-year-old man presented to his GP with a painful red big toe.
The most important diuretic treatment in addition to loops are. The liver metabolizes most components of food and also cleans the blood of bacteria and drugs. ALCOHOLOC LIVER DISEASE Alcoholic liver disease is damage to the liver and its function due to alcohol abuse.
The difficulty of diagnosing drug-induced liver injury is emphasized. Bilirubin a yellowish waste compound was building up in his body and. The two fatal cases of DILI among heavy drinkers involved a 44-year-old man with underlying alcoholic cirrhosis and steatohepatitis who developed acute-on-chronic liver failure 11 days after starting niacin and a 76-year-old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and bronchitis flare who developed severe liver injury and skin rash 6 days after starting azithromycin.
The patient is a healthy 27-year-old man who presented with painless jaundice. The liver is responsible for the absorption of most dietary nutrients as well as the production of growth hormones. After years of alcohol use his liver had stopped filtering his blood.
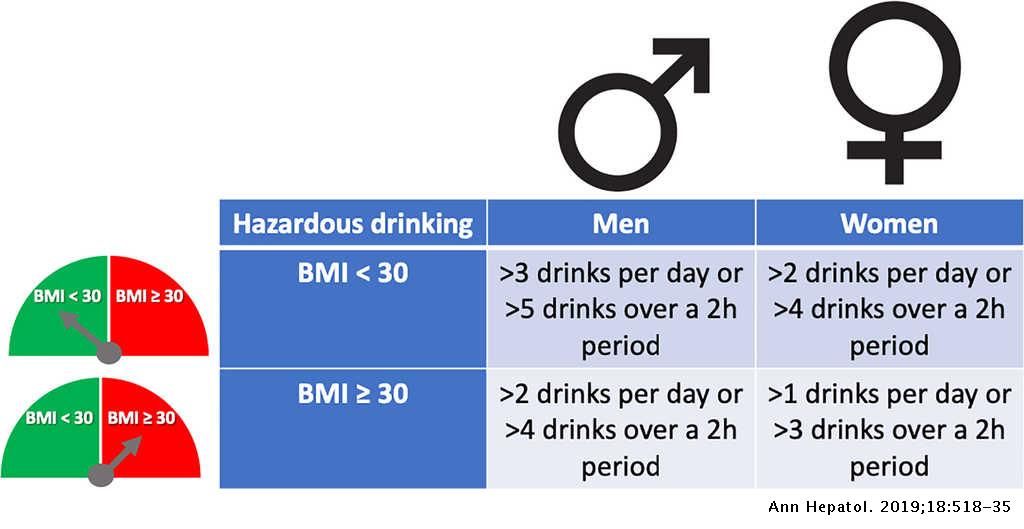
People who drink alcohol daily compared to weekly binge drinkers are at risk of developing more serious forms of liver disease including cirrhosis or progressive fibrosis according to a study done in the United Kingdom. Its the most common alcohol-induced liver problem.
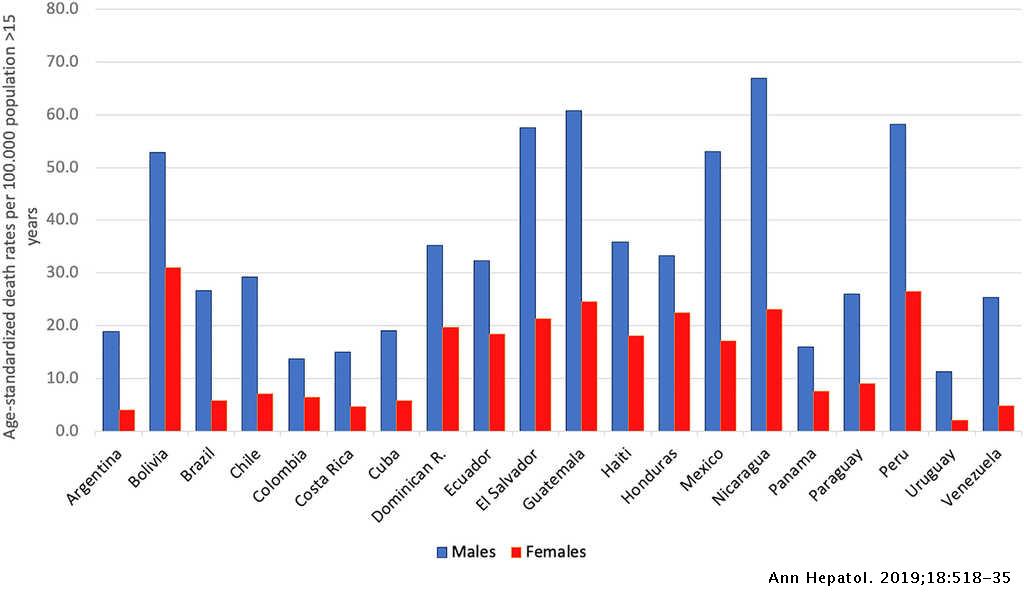
Hol-induced liver disease for both men and women with then those women who develop alcohol-induced liver the steepest increase among women.
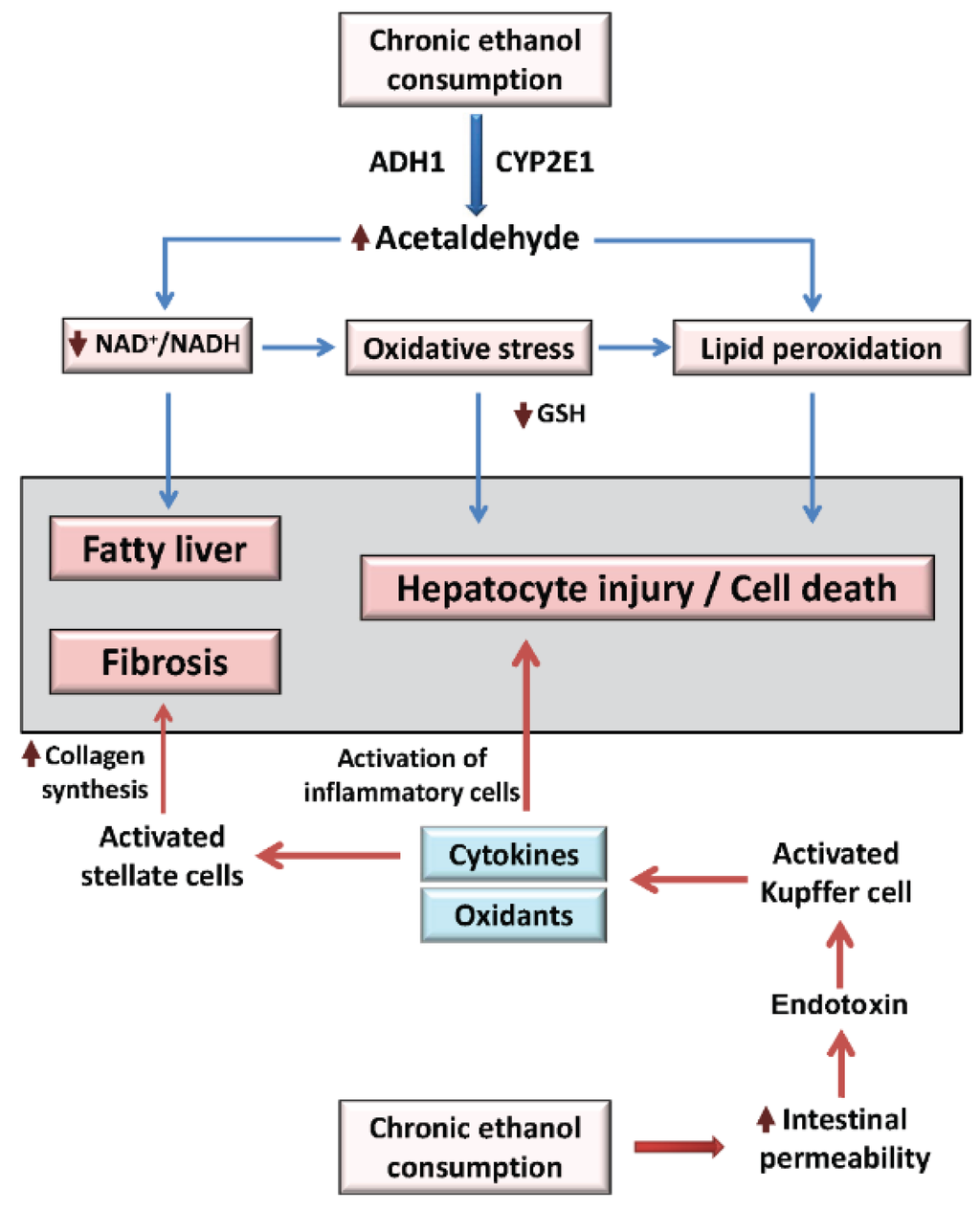
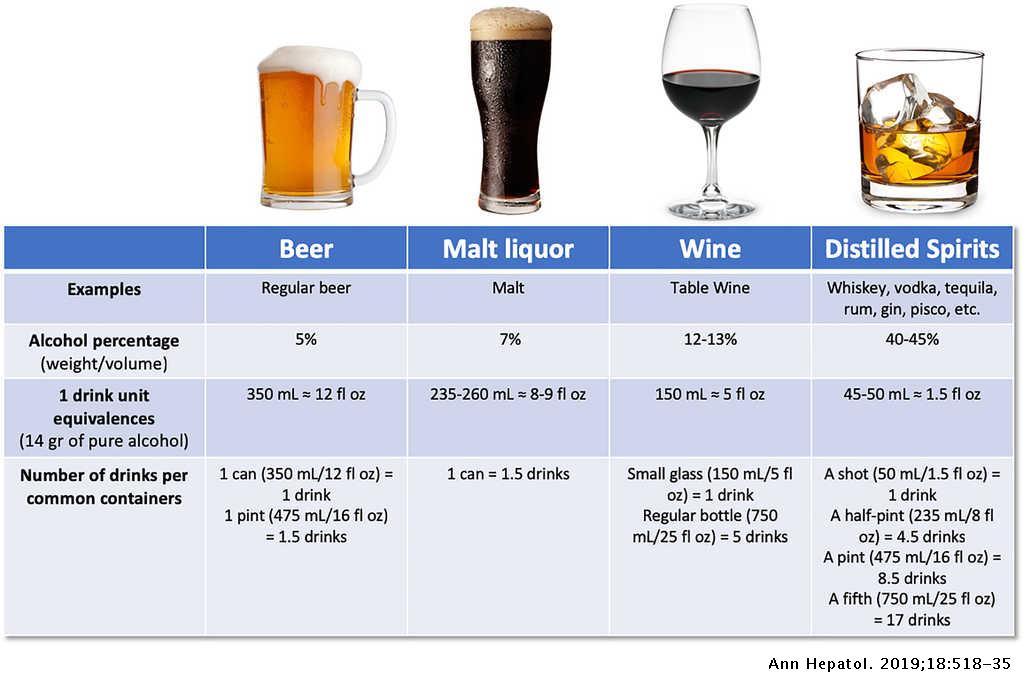
The liver contributes to the metabolism of ingested food and provides the fluids that the GI tract requires. It is usually asymptomatic and is completely reversible once you stop drinking alcohol. Over time scarring and cirrhosis can occur. He had no occupational exposures to solvents was not taking prescription medications and did not use recreational drugs or alcohol. The liver contributes to the metabolism of ingested food and provides the fluids that the GI tract requires. Based on an autopsy series of men a threshold daily alcohol intake of 40 g is necessary to produce pathologic changes of alcoholic hepatitis. Alcoholic liver disease ALD encompasses numerous changes in the liver caused by chronic intake of alcohol since our body cannot store it and possesses limited capacity for degradation. The case study examines Edward a 63 year old man with a history of alcohol- related liver disease ARLD. The patient is a healthy 27-year-old man who presented with painless jaundice.
The two fatal cases of DILI among heavy drinkers involved a 44-year-old man with underlying alcoholic cirrhosis and steatohepatitis who developed acute-on-chronic liver failure 11 days after starting niacin and a 76-year-old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and bronchitis flare who developed severe liver injury and skin rash 6 days after starting azithromycin. Ethanol once ingested through alcoholic-rich beverages is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and transported to the liver the principal organ of alcohol metabolism. It leads to an enlarged liver. The liver contributes to the metabolism of ingested food and provides the fluids that the GI tract requires. It is usually asymptomatic and is completely reversible once you stop drinking alcohol. The two fatal cases of DILI among heavy drinkers involved a 44-year-old man with underlying alcoholic cirrhosis and steatohepatitis who developed acute-on-chronic liver failure 11 days after starting niacin and a 76-year-old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and bronchitis flare who developed severe liver injury and skin rash 6 days after starting azithromycin. Over time scarring and cirrhosis can occur.


































Posting Komentar untuk "A 62 Year Old Man With Alcohol Induced Liver Disease"